Ventricular fibrillation, known commonly as v-fib, is caused by multiple ectopic electrical impulses that depolarize the myocardium in a chaotic fashion. This results in a quivering or fibrillating heart that does not produce a pulse or adequate cardiac output.
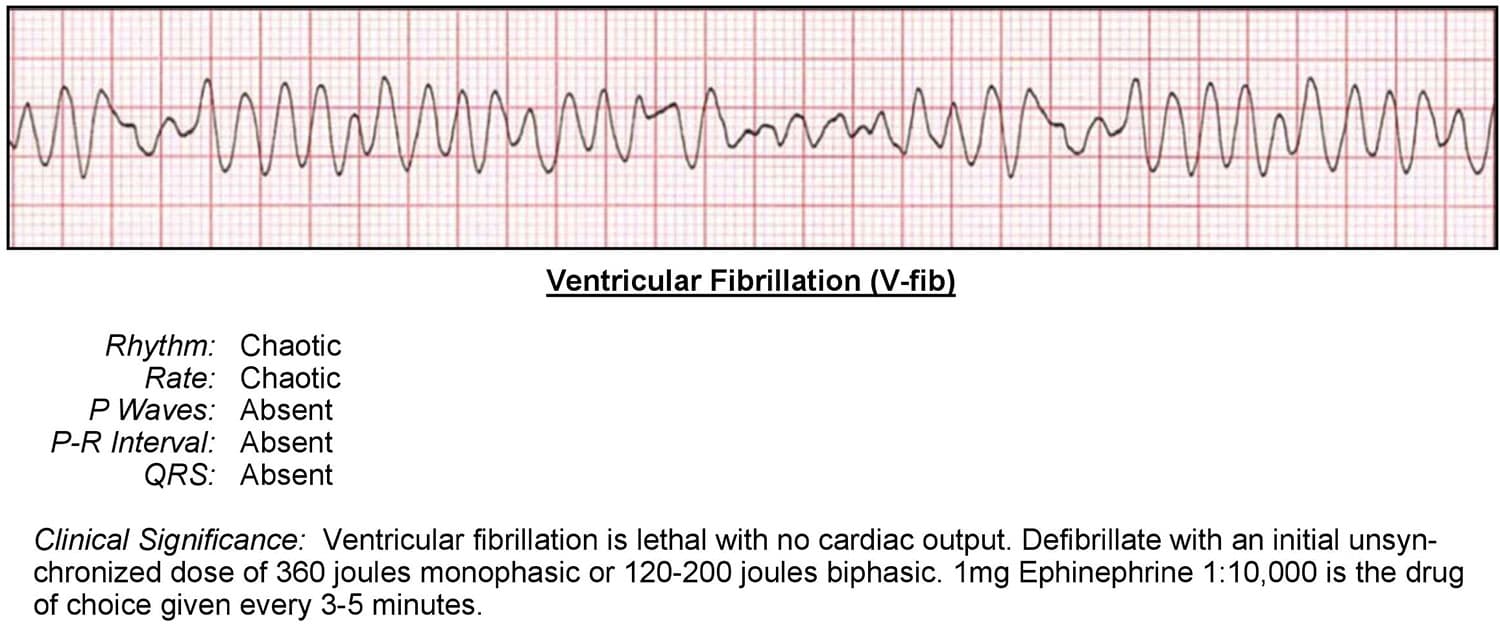
ECG Interpretation:
Rhythm
- Is the rhythm regular or irregular?
- It is irregular
Rate
- What is the rate?
- Between 200-250 bpm
- Is the rate normal, fast, or slow?
- Extremely fast
P Wave
- Are they present?
- There are none. Fibrillatory waves only.
- No other P wave questions are relevant.
PR Interval
- There is no P wave, so there isn’t a PR interval
QRS Complex
- Is the QRS interval less than 0.12 seconds?
- No. Fibrillatory waves only.
- No other QRS questions apply.
Cardiac Interpretation
Ventricular fibrillation is a non-perfusing and lethal dysrhythmia. It is most commonly seen within the first few minutes of cardiac arrest. Because of this, high-quality CPR and immediate defibrillation are vital to increasing the chance for successful resuscitation.